Configuring URLs for multilingual websites
Scenarios described on this page apply only for sites using content tree-based routing.
To see which routing mode is used on your website, open the Settings application -> URLs and SEO and check the Routing section, or consult your website developers.
You can configure the format of URLs on your multilingual site in two ways: using language prefixes or using separate domains.
For example, you can achieve the following format of URLs for two different cultures using language prefixes:
- English – www.example.com/en-us/path
- Spanish – www.example.com/es-es/path
While using separate domains, the URLs can look like this:
- English – www.example.com/path
- Spanish – www.ejemplo.es/path
Using separate domains for different languages
Having a different domain name for each culture is a good way to let visitors know that the particular version of the site is intended for a certain language audience. It is also the best option for multilingual websites with regard to search engine optimization.
For example, if the English version of your site is available under domain.com, the French version could use domain.fr and so on. This scenario uses a different country‑code top‑level domain, but you can set any other domain name format, such as unique subdomains for each culture.
To implement domain separation based on languages you need to first configure the setting:
- Open the Settings application on the URLs and SEO tab.
- Set URL format for multilingual sites to Domain.
- Click Save.
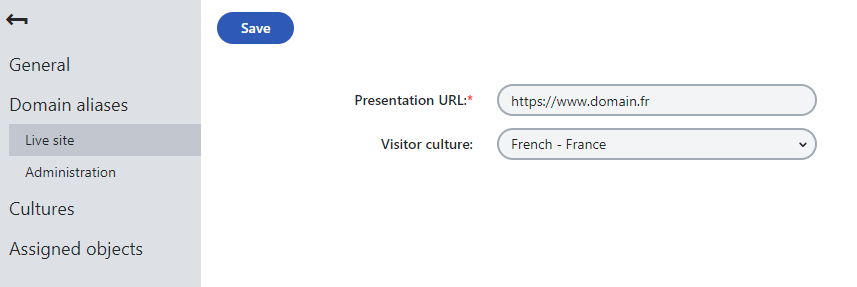
Then, set up the main presentation URL and domain aliases for different languages according to Setting domain names for sites:
- Open the Sites application.
- Edit () your site.
- On the General tab, select your website’s primary language in the Visitor culture field.
- This assigns the given language to the site’s main presentation URL.
- Set up additional domain names for other languages as live site domain aliases on the Domain aliases -> Live site tab.
- Just like with the main domain, you can assign a language to each alias by selecting the matching culture in the Visitor culture field.
Configuration requirements
When setting up the Visitor culture of the site and its aliases, only assign each language to a single domain and do not use the (Automatic) value. Otherwise the system cannot determine which content culture to display.
The system now ensures the following:
- The content culture is selected based on the domain name (presentation URL) through which the website is opened.
- All page URLs are generated using the presentation URL to which the current content culture is assigned.
Authentication with multiple domains
The user context is not carried over when switching between domains on the live site. If you are using standard Forms authentication, registered users who change the content culture while browsing need to log in separately on each language version of the website.
If this is a problem, you can work around it by implementing a single sign-on mechanism for all domains.
Switching between URL formats
When you change the URL format for multilingual sites setting to either the Language prefix or Domain option, URLs are regenerated to comply with the new setting and the old URLs are permanently removed. Therefore, you need to manually handle any broken links or links incorrectly indexed by search engines that could be created by this change.
Using language prefixes for URLs
If you do not own a different domain name for each language version of the website, but still want to ensure unique URLs for each culture, you can use language prefixes. Language prefixes insert a segment into the URL in format <domain>/<language prefix>/<URL path>, for example: <domain>/fr-FR/Home. The language prefix corresponds to the matching culture code by default, but can also be changed to an alias.
To enable language prefixes in your URLs:
- Open the Settings application.
- Select the URLs and SEO settings category.
- Set URL format for multilingual sites to Language prefix.
- Click Save.
If the language prefix URL format is enabled, the system automatically generates URLs containing the appropriate URL prefix for all pages represented in the content tree.
Hiding language prefixes for the default culture
You may want to use URLs without the language prefix for the most used (i.e. the default) content culture. To enable this:
- Open the Settings application.
- Select the URLs and SEO settings category.
- Enable Hide language prefix in default culture URLs.
- Click Save.
All pages with the default content culture will have URLs without the language prefix, i.e. in the format <domain>/<URL path>.
Changing the language prefix text
If you want to change the language prefix for a certain language, the best way is to enable and set culture aliases.
By default, the language prefix matches the culture code of the requested language. To override this behavior:
- Open the Settings application.
- Select the URLs and SEO settings category.
- Enable Use culture alias as language prefix in URLs.
- Click Save.
Continue by setting aliases for your site’s cultures in the Localization application. If a culture alias is set for a language, it takes precedence and the system uses the alias in URL prefixes instead of the culture code.
Culture alias URL collisions
The system does not validate the values set for culture aliases. Make sure aliases do not cause URL collisions with existing URL slugs of pages. For example, a collision can occur if you set a culture alias to English, but already have a page with the English URL slug on the first level of the content tree.
In the case of collisions, the culture alias takes priority in page routing.
For example, to change the language prefix for the French language to France:
- Open the Localization application.
- Select the Cultures tab.
- Typefr-FR into the Culture code filter and click Search.
- Edit () the French - France culture.
- Set the Culture alias property to France.
- Click Save.
The system generates new URLs for all pages in the French culture. The language prefix in page URLs now matches the entered alias, for example <domain>/France/Home instead of <domain>/fr-FR/Home.
Setting page URL slugs for different culture versions
Forcing culture domains or using language prefixes for URLs ensures that you have a different URL for every culture version of each page. You can change URL slugs of pages if you want different culture versions of pages to also have different names in the URL path.
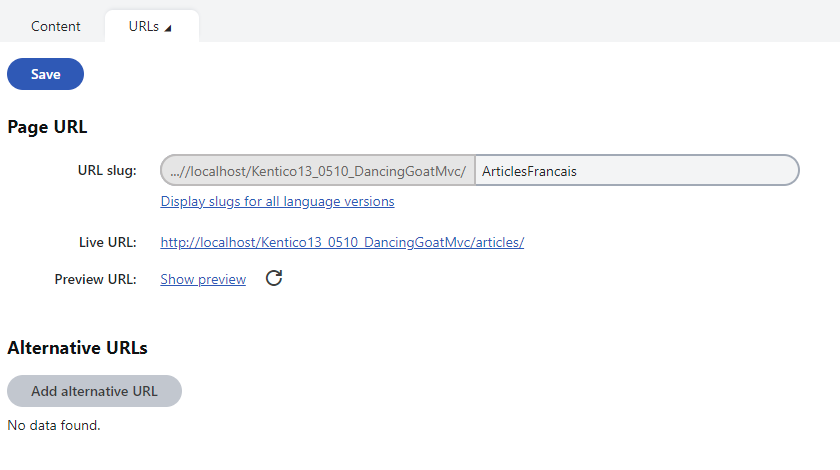
For example, if you want the Articles page in French to have a different URL (slug) than the English version:
- Open the Pages application, and select the Articles page in the content tree.
- Select the French language in the selector below the content tree.
- Open the Properties -> URLs tab.
- In the Page URL section, set the URL slug of the page to /ArticlesFrancais.
- Click Save.
To try out how the custom URL works, sign out and view the English version of the website. If you open the URL <domain>/articlesfrancais (or <domain>/fr-fr/articlesfrancais if you use language prefixes), the website automatically switches the culture to French and displays the French version of the Articles page.
All child pages of the page with the edited slug will also have URLs with the corresponding URL path.
You can also configure various settings related to the format of URLs in the Settings application -> URLs and SEO, such as enforcing lowercase URLs or the use of trailing slash.
See Settings - URLs and SEO for more information.