Configuring Windows AD authentication
The Xperience administration application supports Windows Active Directory integrated authentication. This means that when a user is signed-in to a Windows domain, Xperience automatically recognizes their identity without requiring a user name and password.
When the system successfully authenticates a user via Windows Active Directory for the first time, it automatically creates a matching user account in the Xperience database.
Additionally, the system imports the user’s domain groups as roles. If an existing user is added to new groups in Active Directory, Xperience imports new roles (the update occurs upon reauthentication, i.e. after the user’s session expires). However, existing roles are not removed from users in Xperience when the matching users in Active Directory are removed from groups.
Disabling the automatic role import
If you wish to disable the automatic import of user domain groups as roles in Xperience, add the following key to the /configuration/appSettings section of your project’s web.config file:
<add key="CMSImportWindowsRoles" value="false" />
The imported roles do not authorize the users to perform any actions in Xperience by default. You need to configure permissions and UI personalization settings for the imported roles manually if you wish to use them.
Prerequisite
For Windows authentication to work, the application must be able to access the memberof and userAccountControl attributes of user objects in Active Directory (i.e., the attributes cannot be protected or confidential).
Configuring Windows authentication
Follow the steps below to switch the application to Windows authentication mode:
Edit the web.config file of your administration web project.
Set the mode attribute of the <authentication> element in the <system.web> section to Windows:
<authentication mode="Windows">Save the modified web.config file.
Close all browsers with the Xperience administration interface.
Open a new browser and try to access the administration interface (<site domain>/admin).
- If you encounter a 401 error, continue to the Enabling Windows authentication in IIS section below.
With this configuration, the system automatically authenticates users from Windows Active Directory and imports them to the Xperience database.
You need to manually set up administrator access for your new AD user account.
Sign out button missing with Windows authentication
When Windows authentication is enabled, the Sign out button in user menu in the top right corner of the administration interface is not displayed.
Enabling Windows authentication in IIS
If you are experiencing the 401 error with Windows authentication, you need to enable Windows authentication in your IIS:
Start the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
Locate and select your site in the IIS tree.
Double-click the Authentication icon.
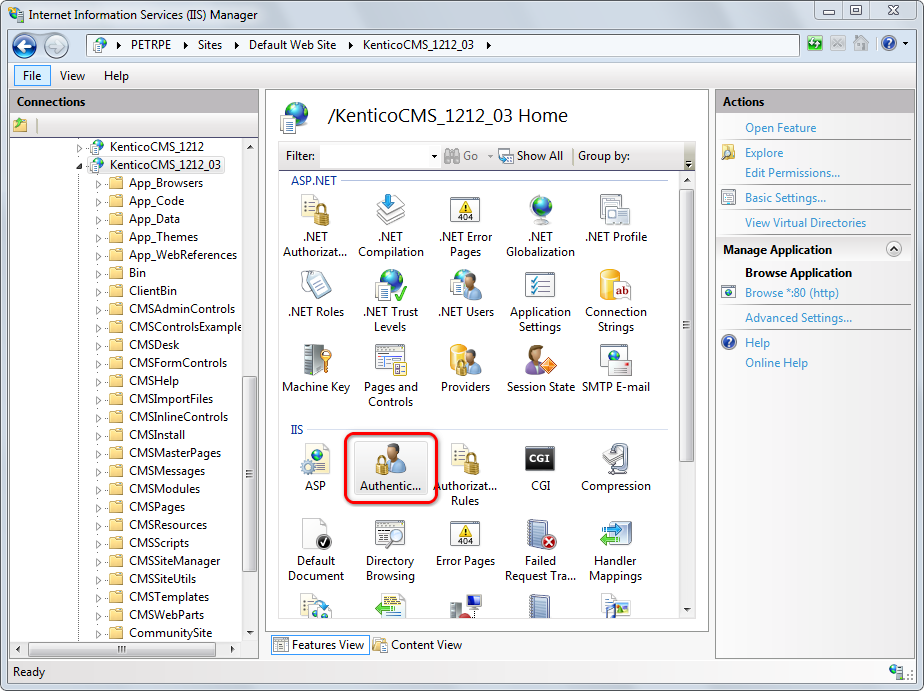
Windows Authentication missing in the list
If your IIS installation does not contain Windows Authentication by default, you need to install it:
- Go to Control Panel -> Programs and Features -> Turn windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services -> World Wide Web Services.
- Under Security, select the Windows Authentication check box.
- Click OK to finish the configuration.Windows Authentication appears as an option in IIS website authentication settings.
Select Windows Authentication.
Click Enable in the Actions menu.
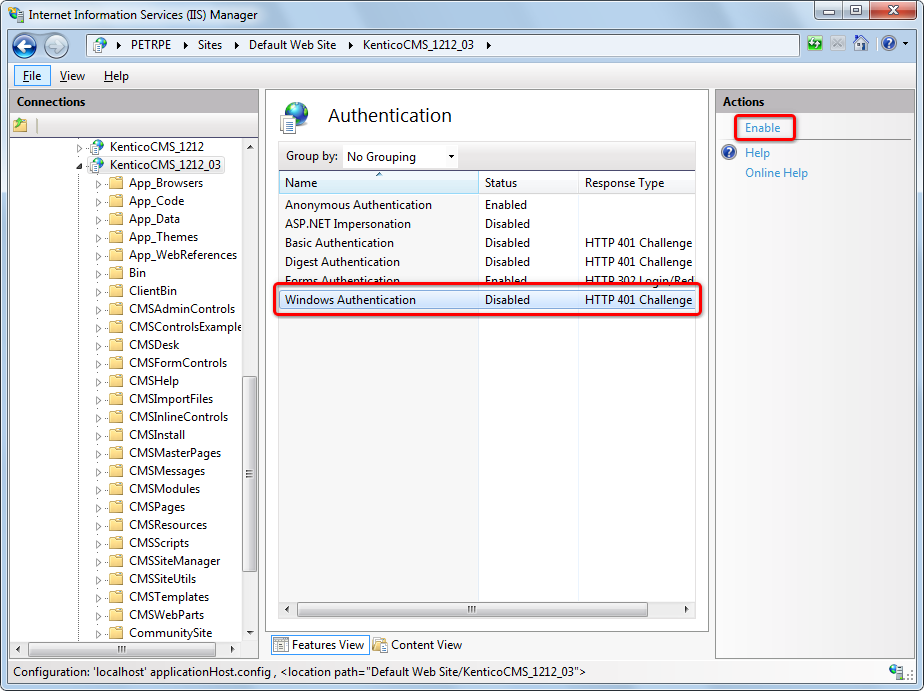
IIS now allows Windows authentication on your site.
Setting up administrator access after enabling Windows authentication
When you access the Xperience administration interface (<site domain>/admin) for the first time after configuring Windows authentication, you will encounter an Access denied message. Windows authentication logs you in under a new user account that the system automatically created based on your Active Directory user name, but the account does not have any permissions.
To allow access to all features as an administrator under Windows authentication, you need to manually grant administrator permissions to your new user account:
- Access the administration interface at least once under Windows authentication (to ensure that the system imports your AD user).
- Edit the project’s web.config file and switch back to Forms authentication (set the mode attribute of the <authentication> element in the <system.web> section back to Forms).
- Sign back in to the administration using forms authentication (under your original administrator account).
- Open the Users application.
- Edit the new user that matches your domain user name (the format is domain-username, for example office-johns).
- On the General tab, set the Privilege level to Global administrator.
- Click Save and sign out.
- Edit your web.config file and switch to Windows authentication again.
Close all browsers. Open a new browser and access the administration interface. Make sure the system recognizes you as a global administrator without the need to manually sign in.
Forbidden character replacement during Active Directory import
When importing users and roles, forbidden characters in the names are replaced by the character defined in Settings -> URLs and SEO -> Forbidden characters replacement.
The default value is a dash “-” (domain-username instead of domain\username). If you are using a different character, please change the entered user name accordingly.
You can override this setting by adding the following keys to the AppSettings section of your web.config file. In both cases, the value must be exactly one character:
<add key="CMSForbiddenUserNameCharactersReplacement" value="-" />
<add key="CMSForbiddenRoleNameCharactersReplacement" value="-" />
Forbidden character replacement can be disabled completely using the following two keys (not recommended).
<add key="CMSEnsureSafeUserNames" value="false" />
<add key="CMSEnsureSafeRoleNames" value="false" />